Rule Engine TS
About
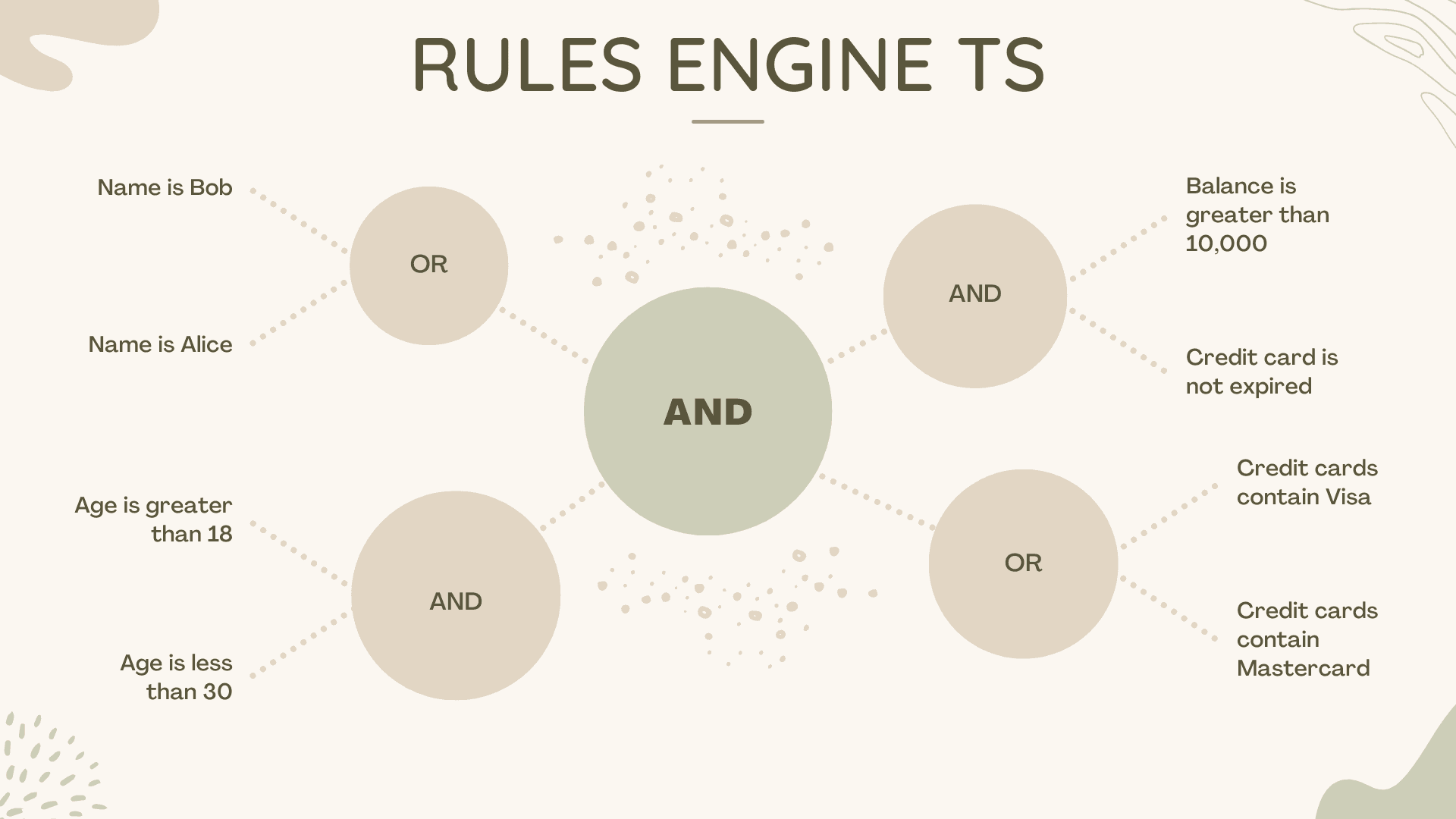
Rules Engine TS is a strongly typed rules engine for evaluating deep and complex rules. With the power of TypeScript, you can create type-safe rules that are easy to read and maintain.
The motivation for this project was to create an out-of-the-box solution that had a simple data structure that was easy to mutate and easy to persist in a database. The general intended use case was to build the rules engine using a user interface, write the rules into a database and in the future retrieve the rules back from the database and run the rules against a target object.
The recommended way to consume rules-engine-ts is in a TypeScript environment. TypeScript will warn you when your rules are missing properties or if the types of your properties are incorrect. That isn't to say that rules-engine-ts can't be run with JavaScript. You will still get autocomplete on the available properties, but you will not get any warnings if you are missing properties or if the types of your properties are incorrect.
Basic usage
A rules engine can be configured and run like so:
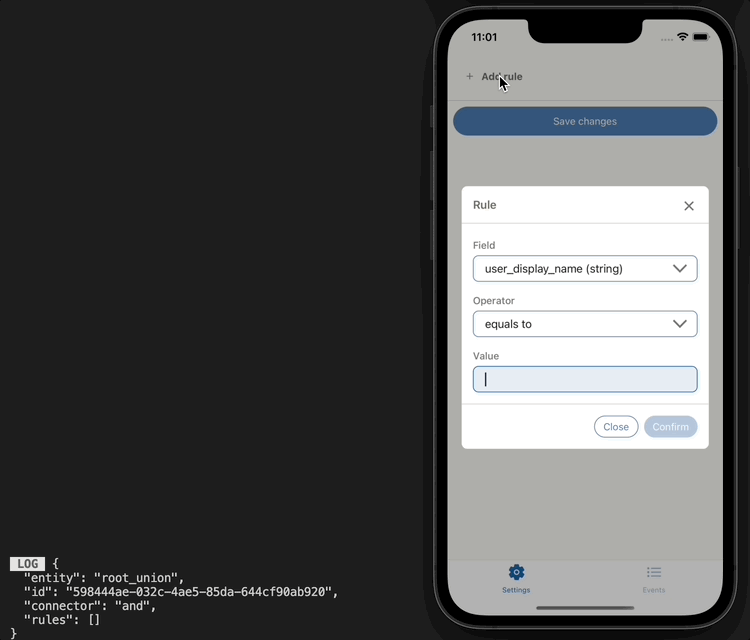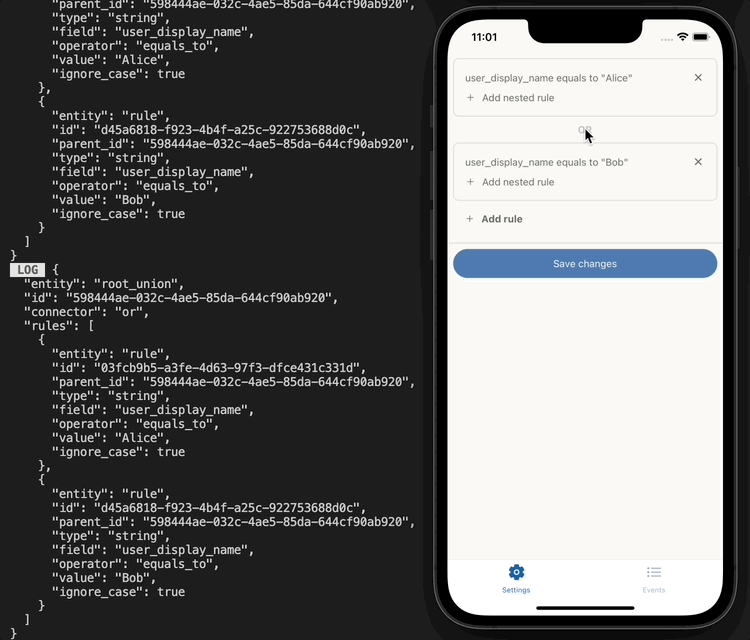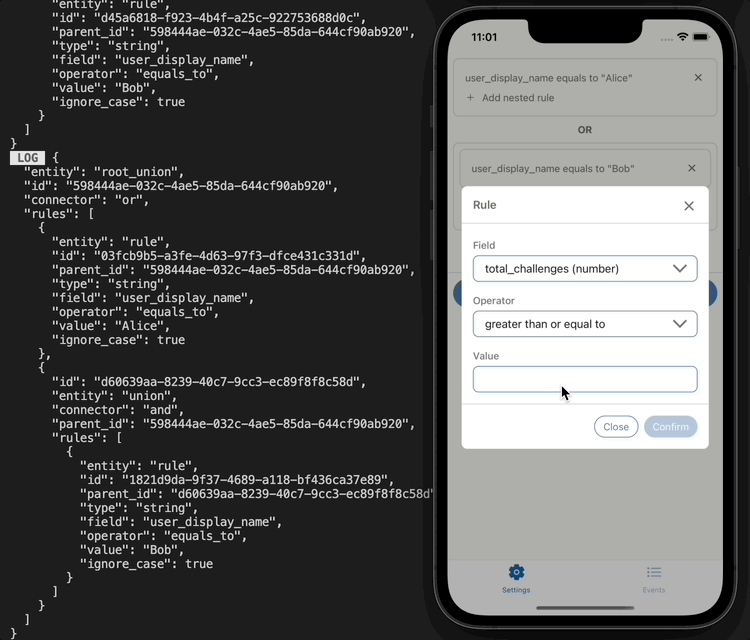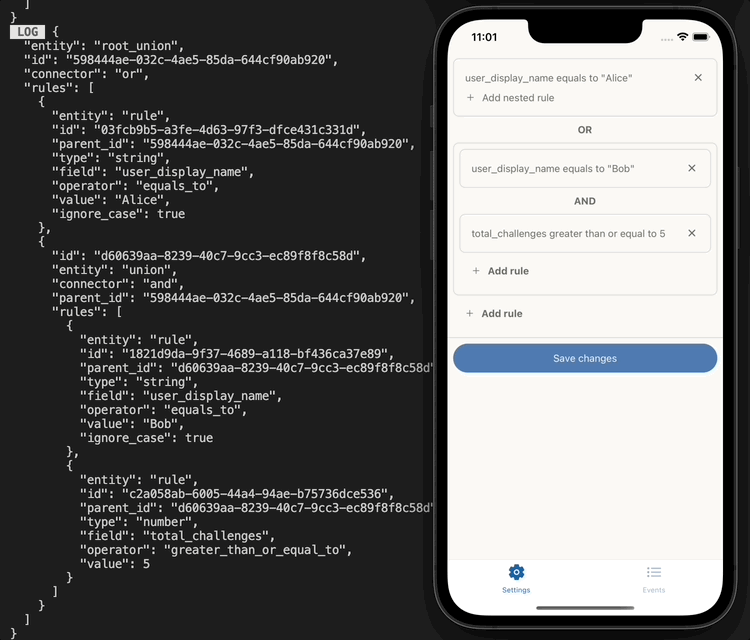
If we console log the root we can see what our rules look like:
UI implementation example
The rules can then be persisted into a database in JSON format:
At a later date, the rules can retrieved from the database and can be run by the rules engine like this:
Open source
The project is Open Source and can be viewed on GitHub & NPM.
Features
- User-friendly API to add complex rules.
- API comes with helper functions to add, remove or update rules and unions.
- Recursively search for any nested rule or union.
- Uses a simple concept called Unions to join rules.
- Decision tree-like data structure.
- No limitations on the levels of nesting.
- Rules are strongly typed with the help of discriminated unions.
- Validator function that verifies all properties are correct.
Technologies used
- Zod - Validation library.
- Zod Error - Error renderer.
- Node.js - Runtime environment.
- TypeScript - Written 100% in TypeScript.
To do
- Create recipe examples.
- Create a function to detect conflicting or redundant rules.
- Create a UI builder tool.